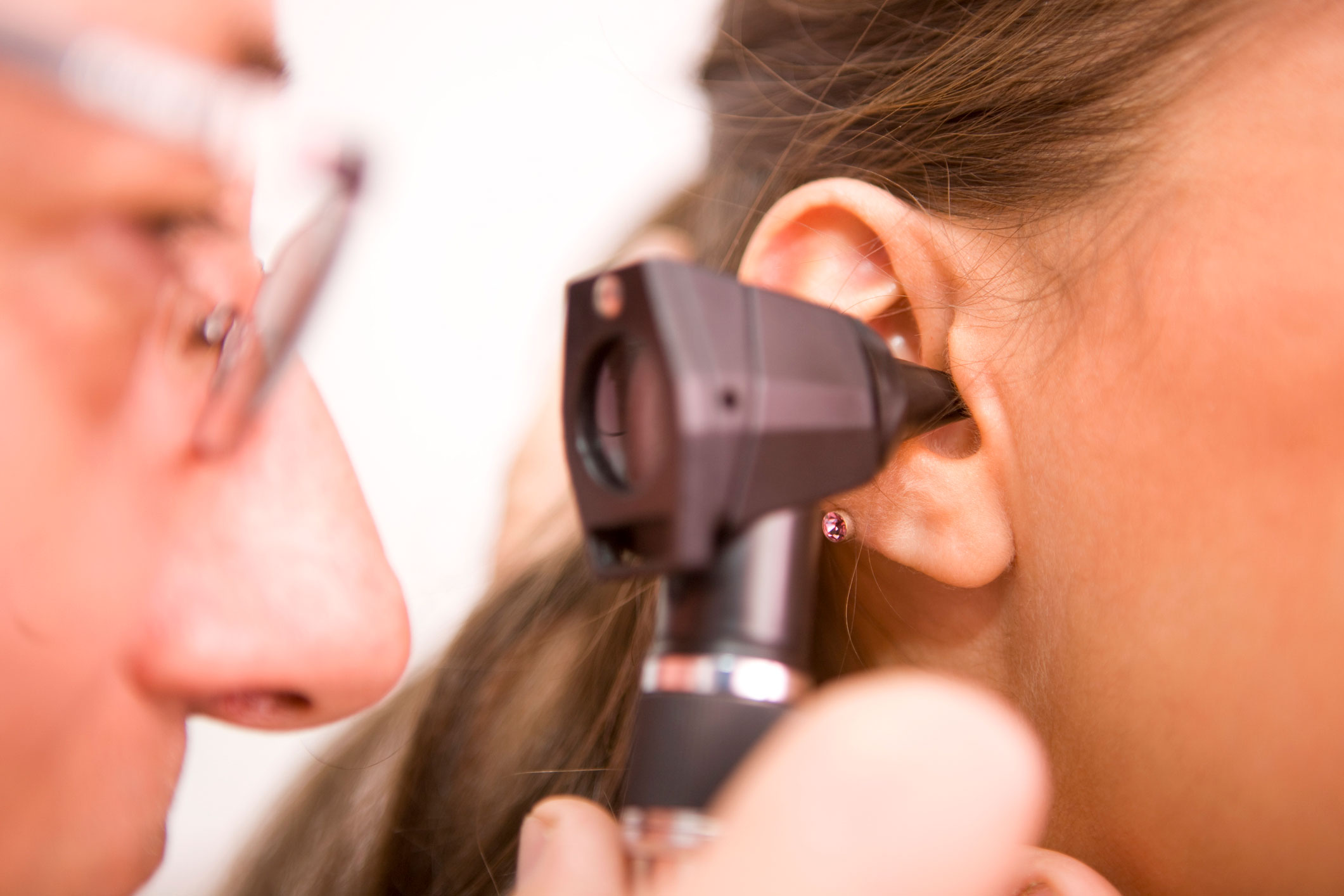
Ear Syringe
What is ear wax?
Ear wax is the product of ceruminous and oil gland secretions, mixed with exfoliated skin cells. It forms a protective film, has antibacterial properties and provides lubrication to the ear canal. It is the ear’s self-cleaning mechanism, and traps dust and dirt, which are then excreted from the ear canal.
Why does ear wax accumulate?
In some situations wax accumulates and can become impacted. Narrowing or obstruction of the ear canal, due to anatomical variations or infectious or dermatological diseases, can interfere with the normal migratory process that leads to wax excretion from the ear canal.
Irritation from foreign objects placed in the ear (eg cotton tips, hearing aids and ear plugs) can cause chronic changes to the skin of the ear canal and impair the normal excretion of wax from the ear canal. Cotton buds also tend to push ear wax deeper into the ear canal, and hearing aids and ear plugs obstruct the ear canal and contribute to wax accumulation over time. Furthermore, the ceruminous glands atrophy with age and produce a drier wax that migrates more slowly.
Ear wax impaction is present in up to 57% of older patients, compared with 5% of younger, healthy adults.
When do we require ear syringe?
Ear wax accumulation is normal and does not require treatment unless it is symptomatic.
Ear syringe is appropriate when ear wax becomes impacted, obscuring visualisation of the ear drum, and is associated with symptoms.
Common symptoms include:
- hearing loss
- ear pain
- itching
- fullness
- dizziness
- tinnitus
- cough
Ear syringe is also often required to allow view of the ear drum for diagnostic purposes, or to allow for accurate hearing testing (audiometry),